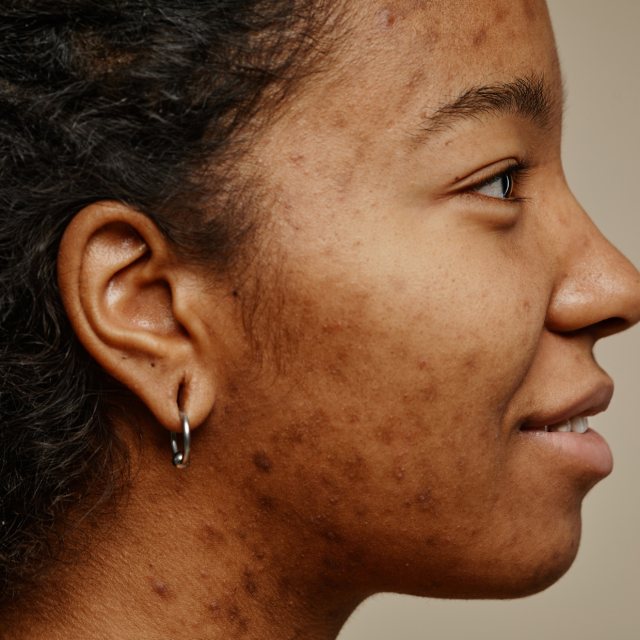

Uneven skin tone and pigmentation issues are common skin concerns that affect people of all ages and skin types. Hyperpigmentation can feel challenging, as these visible patches often impact self-confidence and may seem difficult to treat.
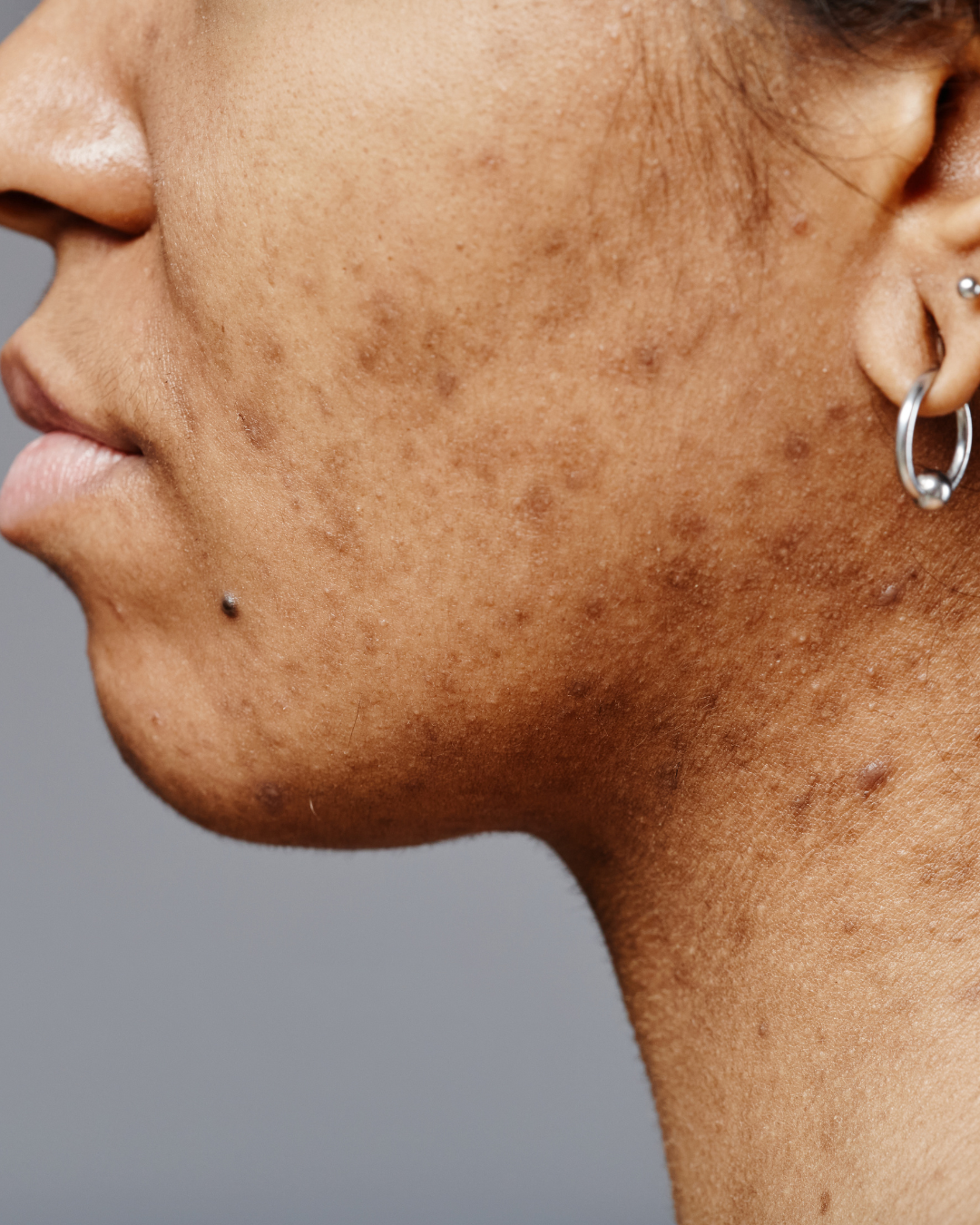
Skin Pigmentation refers to darkened areas of skin that occur due to excess production of melanin, the pigment responsible for giving skin its colour. These darker patches can vary in size, shape, and intensity and are typically more noticeable on exposed areas like the face, neck, hands, and shoulders. Hyperpigmentation can create an uneven skin tone that stands out against the natural complexion, often leading people to seek a hyperpigmentation treatment that goes beyond typical skincare products.
Skin Pigmentation can appear in different forms, each with unique patterns and causes.
Sunspots or age spots, also known as solar lentigines, are one of the most common types of sun damage, forming due to repeated sun exposure that triggers melanin production. These spots typically appear as small, round, brown patches on areas of skin that get a lot of sunlight.
Melasma, another form of pigmentation, usually results from hormonal changes. This type is characterised by larger, darker patches, often on the cheeks, forehead, and upper lip, and is more common in women experiencing hormonal shifts due to pregnancy or birth control.
Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH) arises after skin trauma, such as acne or minor injuries, leaving discoloured marks that can take months or even years to fade.
Each type of pigmentation can present unique challenges and often requires a specific, targeted approach to reduce its appearance effectively.
Pigmentation is influenced by several factors, including both internal and external elements that can stimulate melanin production. Exposure to UV rays from the sun is the primary factor in hyperpigmentation, as UV exposure prompts skin cells to produce more melanin as a protective measure. Over time, this can result in sunspots or age spots, particularly on skin that isn’t adequately protected. Wearing sunscreen daily and avoiding prolonged exposure are key preventative steps, but pigmentation can still develop even with diligent care.
Hormonal fluctuations are another common cause, especially for conditions like melasma. During pregnancy, for instance, increased estrogen and progesterone levels can cause melanin cells to become overactive, leading to the development of dark patches on the face. Hormonal birth control pills and hormone replacement therapy can similarly affect melanin production. Additionally, skin trauma, such as from acne, burns, or certain skincare treatments, can result in post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation, as the skin produces extra pigment while healing. Genetics also play a role; some individuals have a genetic predisposition to produce more melanin or are more prone to pigmentation changes due to their skin type.
Each of these factors contributes differently to the formation of pigmentation, and often, multiple factors are at play, making pigmentation particularly persistent. However, with the right approach, pigmentation can be managed effectively. Our treatments at SRGN Clinic are designed to target these underlying causes, helping clients achieve long-term, visible improvements in skin tone and clarity.
SylfirmX is a breakthrough treatment that combines micro-needling with radio-frequency energy to target pigmentation and improve overall skin tone. The treatment works by delivering targeted energy to the deeper layers of the skin, breaking down excess pigment and encouraging the production of new, evenly toned skin cells. Sylfirm X is especially effective for reducing melasma and other forms of pigmentation, with minimal downtime and noticeable results over a series of treatments.
Chemical Peels are a highly effective option for treating superficial pigmentation and creating an even skin tone. During this treatment, a customised chemical solution is applied to exfoliate the outer layers of the skin, reducing the appearance of dark spots and revealing fresher, lighter skin beneath. Our team selects the appropriate peel strength to address the type and depth of pigmentation, providing a safe and targeted treatment that improves both pigmentation and overall skin texture.
Microneedling with Dracula Facial offers a natural, regenerative approach to pigmentation treatment. Microneedling creates microchannels in the skin, allowing Dracula Therapy to penetrate deeply and promote healing and collagen production. Dracula Therapy’s natural growth factors work to brighten and renew the skin, helping to reduce pigmentation and improve overall skin tone and texture. This combined treatment is particularly beneficial for post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation, giving the skin a balanced and radiant appearance.
The best treatment depends on the type and depth of your pigmentation. Options like SylfirmX (microneedling with radio-frequency), chemical peels, and microneedling with Dracula Facial are highly effective.
Targeted treatments like chemical peels or radio-frequency microneedling can help break down pigment, while consistent use of sunscreen and vitamin C can prevent dark spots from worsening.
For quicker results, treatments like chemical peels or professional-grade microneedling work well. At-home options, such as vitamin C serums and retinol, can also help lighten pigmentation over time.
Many treatments can reduce or even eliminate pigmentation, but it may return with sun exposure or hormonal changes. Consistent care, like using SPF, helps keep it from coming back.
Yes, vitamin C is great for brightening skin and reducing the appearance of dark spots. It can be used daily to gradually lighten pigmentation and improve overall tone.
It varies, but with professional treatments, you might see noticeable improvement within a few weeks. Topical treatments, like vitamin C, often take a couple of months for significant results.
In-office treatments like chemical peels and SylfirmX tend to work faster than topical treatments alone, as they target deeper layers of the skin.
If your hyperpigmentation isn’t fading, it could be due to factors like sun exposure, underlying skin conditions, or inconsistent use of treatments and SPF.
Sun exposure is often the biggest culprit, but hormonal changes or irritation from certain skincare products can also make pigmentation worse.
Hyperpigmentation can arise from factors like sun exposure, hormonal shifts, inflammation, or even stress. Our practiotioners can help identify the exact cause and recommend treatments.